MISC
1、Phishing
先使用CHMunpacker获取到包含的文件
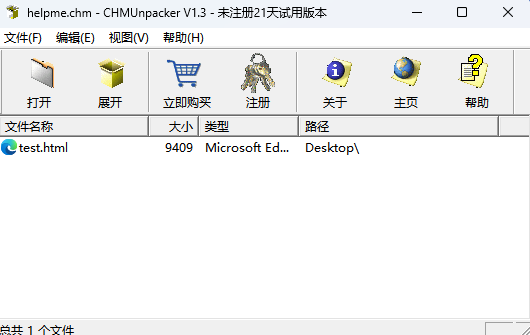
获取到文件后,发现是将一堆字节写入一个zip文件,我们利用脚本实现
# Retry extraction with a more robust pattern
import re, base64, zipfile
from pathlib import Path, PurePosixPath
html_path = Path("test.html")
out_zip = Path("reversed.zip")
extracted_dir = Path("reversed_extracted")
actions = []
html = html_path.read_text(encoding='utf-8', errors='replace')
m = re.search(r'var\s+command\s*=\s*"([^"]*)";', html, flags=re.DOTALL)
if not m:
raise ValueError("Could not find var command = \"...\" in the HTML.")
cmd_str = m.group(1)
actions.append(f"Full command string length: {len(cmd_str)}")
# Try to extract the payload between 'echo ' and ' > reversed.zip'
m2 = re.search(r'echo\s+(.+?)\s*>\s*reversed\.zip', cmd_str, flags=re.DOTALL)
if not m2:
# maybe no spaces before >
m2 = re.search(r'echo\s+(.+?)>\s*reversed\.zip', cmd_str, flags=re.DOTALL)
if not m2:
# fallback: remove leading 'echo ' and trailing ' > reversed.zip' if present by endswith checks
if cmd_str.startswith("echo "):
payload = cmd_str[5:]
# remove trailing '> reversed.zip' if present
payload = re.sub(r'\s*>\s*reversed\.zip\s*$', '', payload)
else:
payload = cmd_str
else:
payload = m2.group(1)
payload = payload.strip()
actions.append(f"Extracted payload length: {len(payload)}")
# Attempt base64 decode of payload
b64 = re.sub(r'\s+', '', payload)
decoded = None
for pad in ("", "=", "==", "==="):
try:
decoded = base64.b64decode(b64 + pad, validate=True)
actions.append(f"Base64 decode succeeded with padding '{pad}'. Decoded bytes: {len(decoded)}")
break
except Exception as e:
pass
if decoded is None:
actions.append("Base64 decode failed; trying latin-1 bytes fallback.")
decoded = payload.encode('latin-1', errors='ignore')
out_zip.write_bytes(decoded)
actions.append(f"Wrote {out_zip} ({out_zip.stat().st_size} bytes)")
is_zip = False
try:
with zipfile.ZipFile(out_zip, 'r') as zf:
is_zip = True
actions.append("reversed.zip is a valid zip. Contents:")
for name in zf.namelist():
actions.append(" - " + name)
extracted_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
zf.extractall(path=extracted_dir)
except zipfile.BadZipFile:
actions.append("reversed.zip is NOT a valid zip file (BadZipFile).")
except Exception as e:
actions.append(f"Error trying to open zip: {e}")
print("=== ACTIONS ===")
for a in actions:
print(a)
if is_zip:
# search extracted files for flag patterns
patterns = [r'FLAG\{.*?\}', r'flag\{.*?\}', r'CTF\{.*?\}', r'FLAG: ?\S+', r'flag: ?\S+']
found = []
for p in extracted_dir.rglob("*"):
if p.is_file():
b = p.read_bytes()
for enc in ('utf-8','latin-1','cp1252'):
try:
text = b.decode(enc)
break
except:
text = None
if text:
for pat in patterns:
for mm in re.finditer(pat, text, flags=re.IGNORECASE|re.DOTALL):
found.append((p.name, mm.group(0)))
if found:
print("\nFound flag-like patterns:")
for f in found:
print(f" - {f[0]} : {f[1]}")
else:
print("\nNo flag-like patterns in extracted files.")
else:
# If not zip, try checking decoded bytes for ZIP signature anywhere and extract that slice
data = decoded
idx = data.find(b'PK\x03\x04')
if idx != -1:
candidate = out_zip.parent / "embedded_part.zip"
candidate.write_bytes(data[idx:])
print(f"\nFound ZIP signature at offset {idx}, wrote to {candidate}")
try:
with zipfile.ZipFile(candidate, 'r') as zf:
print("embedded_part.zip contents:", zf.namelist())
zf.extractall(path=extracted_dir)
print("Extracted to", extracted_dir)
except Exception as e:
print("Could not open embedded_part.zip:", e)
else:
print("\nNo ZIP signature found in decoded bytes.")然后我们可以成功获取到一个损坏的ZIP文件,注意观察其十六进制文件,我们可以看到这个文件字节被反转了
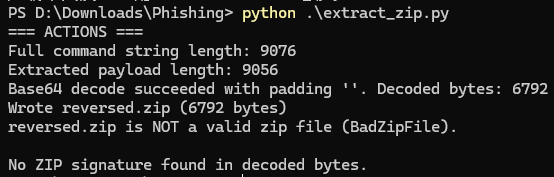
我们来修复一下
# Try reversing the decoded bytes and checking for ZIP signature / opening as zip.
from pathlib import Path
import zipfile
in_path = Path("reversed.zip")
rev_path = Path("reversed_fix.zip")
data = in_path.read_bytes()
rev = data[::-1]
rev_path.write_bytes(rev)
print("Wrote reversed bytes to", rev_path, "size", rev_path.stat().st_size)
import zipfile, io
try:
with zipfile.ZipFile(rev_path, 'r') as zf:
print("rev zip contents:", zf.namelist())
zf.extractall(path="reversed_extracted")
print("Extracted to reversed_extracted")
except zipfile.BadZipFile as e:
print("reversed_fix.zip is NOT a valid zip:", e)
# check for ZIP signature in rev
idx = rev.find(b'PK\x03\x04')
print("ZIP signature index in reversed bytes:", idx)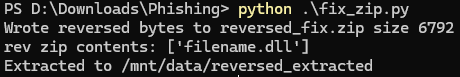
修复成功,并且发现其中有一个文件filename.dll,我们继续提取
# Try reversing the decoded bytes and checking for ZIP signature / opening as zip.
from pathlib import Path
import zipfile
in_path = Path("reversed.zip")
rev_path = Path("reversed_fix.zip")
data = in_path.read_bytes()
rev = data[::-1]
rev_path.write_bytes(rev)
print("Wrote reversed bytes to", rev_path, "size", rev_path.stat().st_size)
import zipfile, io
try:
with zipfile.ZipFile(rev_path, 'r') as zf:
print("rev zip contents:", zf.namelist())
zf.extractall(path="reversed_extracted")
print("Extracted to reversed_extracted")
except zipfile.BadZipFile as e:
print("reversed_fix.zip is NOT a valid zip:", e)
# check for ZIP signature in rev
idx = rev.find(b'PK\x03\x04')
print("ZIP signature index in reversed bytes:", idx)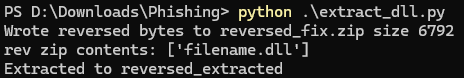
提取成功,由于DLL 是 Windows 的 PE 文件,内部所有「宽字符串」(wchar_t*)在内存/文件中的字节序都是 UTF-16LE。所以我们用该编码搜索字符串
# Extract a larger UTF-16LE region around the found index and search for flag{...} pattern
from pathlib import Path, re
f = Path("reversed_extracted/filename.dll")
data = f.read_bytes()
# find utf-16le 'f\0l\0a\0g\0' index
idx = data.find(b'f\x00l\x00a\x00g\x00')
start = max(0, idx-500)
end = min(len(data), idx+2000)
seg = data[start:end]
text = seg.decode('utf-16le', errors='ignore')
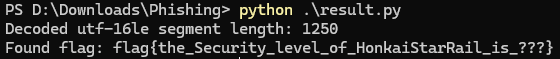
print("Decoded utf-16le segment length:", len(text))
m = re.search(r'flag\{.*?\}', text, flags=re.IGNORECASE|re.DOTALL)
if m:
print("Found flag:", m.group(0))
else:
# print the decoded segment to inspect
print("No full flag found by simple regex. Showing decoded segment:\n")
print(text[:2000])获得flag
2、DNS分身术
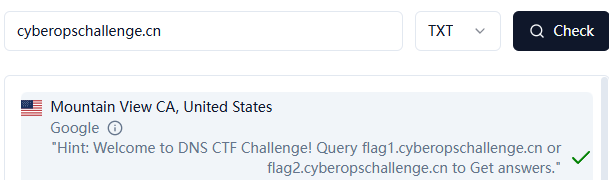
题目可知,本体的flag应该是在DNS解析中,我们先去查询,字符串大概率是TXT解析。
发现flag1和flag2,我们先查flag1
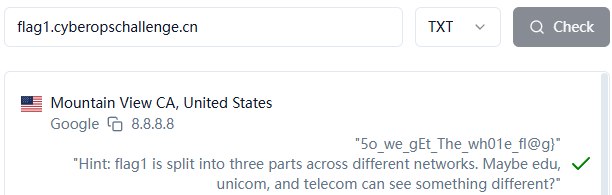
找到最后一段flag和告诉我们使用不同网络,我们使用ITdog,因为他有联通线路,找到中间段

最前一段需要教育网,那么我们指定客户端子网地址,使用上海交大的DNS,得到flag前段
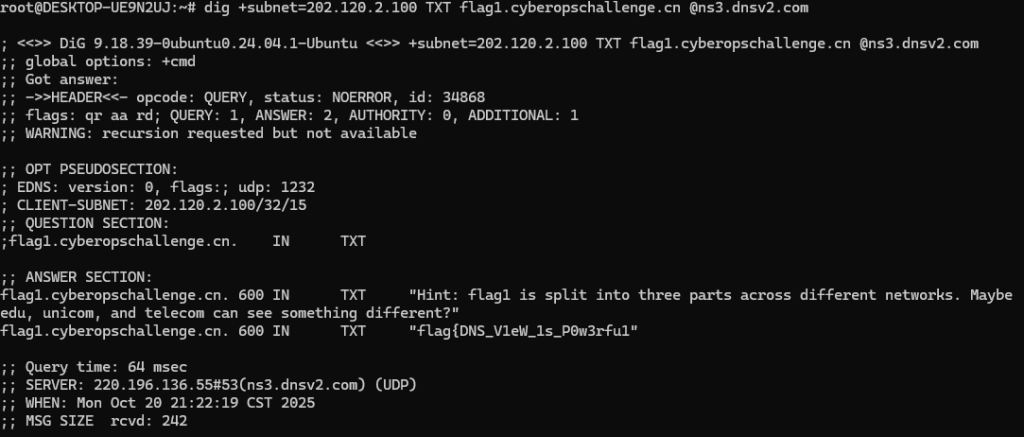
所以得到flag1:flag{DNS_V1eW_1s_P0w3rfu1_1t_depends_0n_ECS_5o_we_gEt_The_wh01e_fl@g}
接下来flag2,同样方法,看到提示
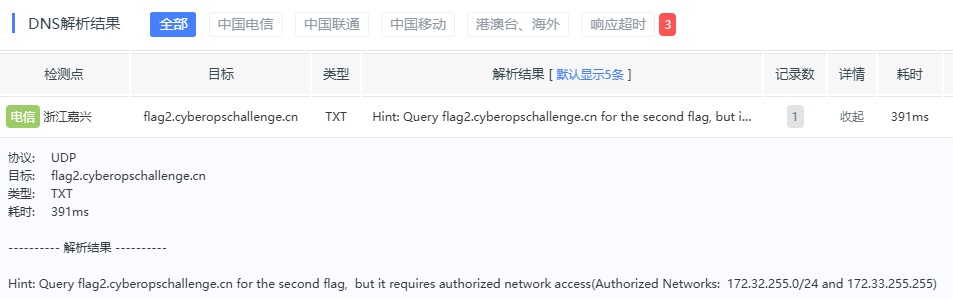
发现只有受认证网络才能看到,那我们就使用172.32.255.255
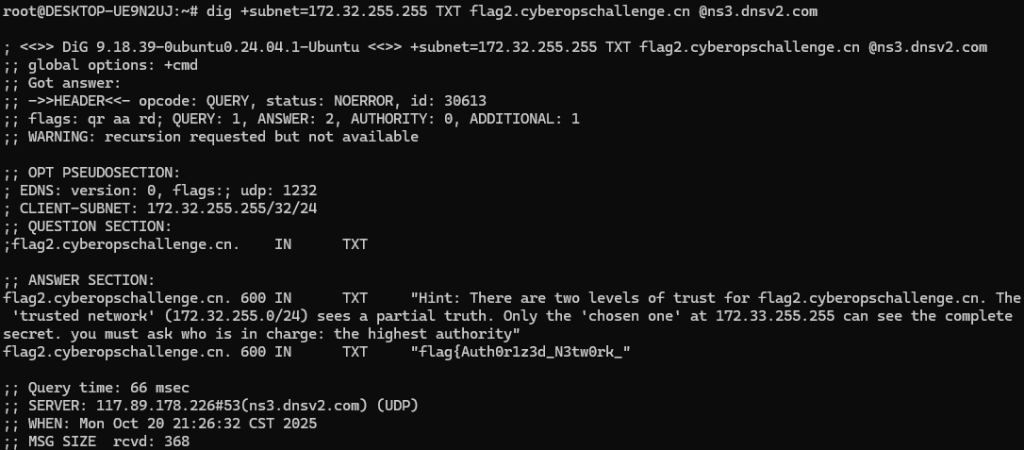
然后再使用另一个授权地址获取到另一半flag即可
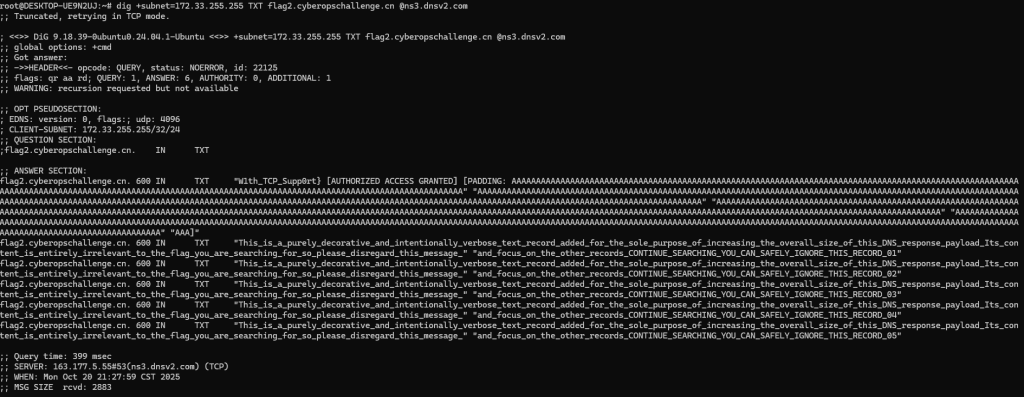
所以flag2:flag{Auth0r1z3d_N3tw0rk_W1th_TCP_Supp0rt}
3、网络运维小助手
本题属于大模型Prompt逆向工程,我们需要获取到两个安全密钥

解码得到第一个密钥 flag{S@y-the-w0rd}
然后获得第二个密钥,现在需要在开启知识库的情况下询问,我们可以利用第一个密钥获得管理员身份,然后读取第二个

flag{RAG-w3ll-h@cked}
Reverse
校园网络保卫战
flag1:这个flag是从远端获取flag,然后进行解密后与用户输入进行对比,若相同,则正确,我们先通过抓包得到具体请求地址,这里使用burpsute+proxifier的组合,设置过程就不赘述,在输入flag1后,抓取到请求地址
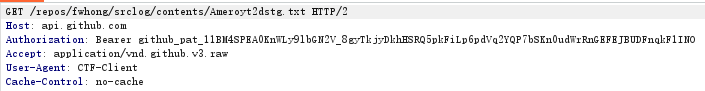
我们使用repeter重放请求获得密文
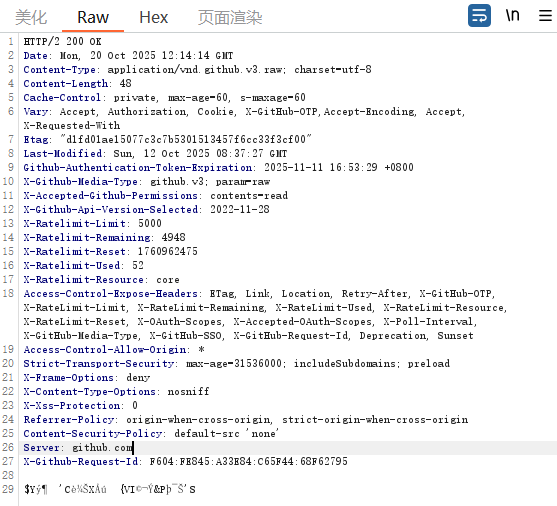
显然是一段乱码,不方便,我们转十六进制。然后我们找到加密逻辑并逆向。先是用百度做了连通性检查,然后携带请求头访问目标网址,那么接下来显然就是加密与对比,找到加密逻辑
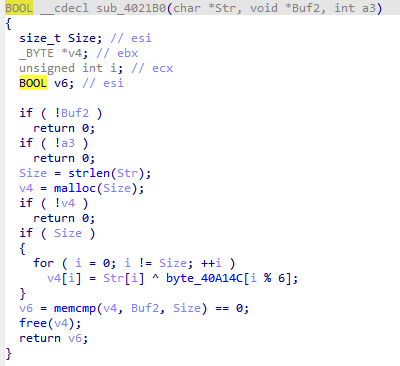
注意到有异或,获取异或的对象内容byte_40A14C,解密即可
data = [0x24,0x59,0x19,0xc3,0xbd,0xc2,0xb6,0xc2,0x9d,0x27,0x43,0x1d,
0xc3,0xa8,0xc2,0xbe,0xc5,0xa0,0x1d,0x58,0x1d,0xc3,0x85,0xc3,0xba,
0xc2,0x8d,0x7b,0x56,0x49,0xc2,0xa9,0xc2,0xac,0xc3,0x9d,0x26,0x50,
0x19,0xc3,0xbe,0xc2,0xaf,0xc5,0xa0,0x27,0x53,0x05]
key = [0x42,0x35,0x78,0x9A,0xCD,0xEF]
# 把给定字节当作原始字节流的 UTF-8 表示,先解码成 Unicode 字符
b = bytes(data)
s = b.decode('utf-8', errors='replace')
# 用每个 Unicode 字符的低 8 位 (ord(ch) & 0xFF) 作为原始字节(处理被多字节编码的情况)
orig = [ord(ch) & 0xFF for ch in s]
# XOR 还原明文
plain = bytes([orig[i] ^ key[i % len(key)] for i in range(len(orig))])
print(plain) # 可见原始 bytes
print(plain.decode('utf-8', errors='replace')) # 可读形式
虽然有不可见字符,但是很容易看出其为e,结束。
flag2:
第二题是硬编码的flag,查找字符串,发现flag2判断逻辑
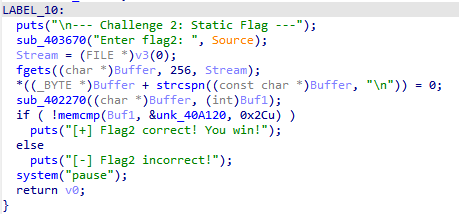
通过sub_402270加密的数据,与&unk_40A120密文对比,若相同则对,那么就是说用&unk_40A120逆向即可得到flag,查看sub_402270函数逻辑,把这个当成密钥种子扩建成 256 字节的自定义 S 盒。
这个s盒是非标准的,是作者自己写的一个逻辑:以 16 字节种子为起点,循环 16 次,每次都算出一组新的 16 字节 → 拼成 256 字节数组 S[0…255]。
题目对flag进行了4层加密:
1、首先是逐字节和0x33进行异或
2、把字节当做s盒的下标,取出s[]当做密文字节,就是s盒替换
3、之后将结果循环右移3位
4、最后在xor (i – 86)&0xFF
找到种子
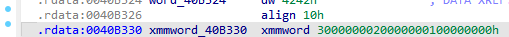
逆向得到S盒,从而解出flag
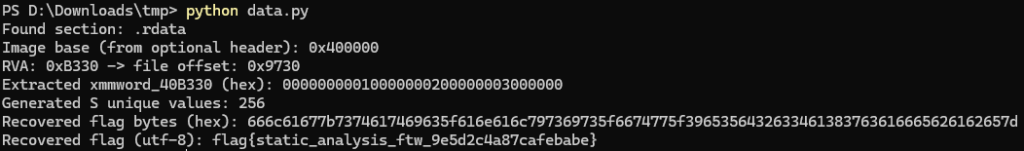
# Extract xmmword_40B330 from uploaded PE at VA 0x0040B330, build S and recover flag bytes.
# This runs in the notebook environment and reads malware.exe provided earlier.
from binascii import hexlify
import struct, sys, os
PE_PATH = 'malware.exe'
VA_target = 0x0040B330 # address from disassembly
IMAGE_BASE_HINT = 0x400000 # typical
if not os.path.exists(PE_PATH):
raise SystemExit(f"PE file not found at {PE_PATH}")
data = open(PE_PATH, 'rb').read()
def read_u16(buf, off): return struct.unpack_from('<H', buf, off)[0]
def read_u32(buf, off): return struct.unpack_from('<I', buf, off)[0]
# Parse DOS header
if data[:2] != b'MZ':
raise SystemExit("Not a PE (MZ header missing)")
e_lfanew = read_u32(data, 0x3C)
if data[e_lfanew:e_lfanew+4] != b'PE\x00\x00':
raise SystemExit("Invalid PE signature")
# COFF header
machine = read_u16(data, e_lfanew+4)
num_sections = read_u16(data, e_lfanew+6)
size_optional = read_u16(data, e_lfanew+20)
optional_header_offset = e_lfanew + 24
magic = read_u16(data, optional_header_offset)
# determine 32/64-bit
is_pe32_plus = (magic == 0x20B)
if is_pe32_plus:
image_base = read_u64 = struct.unpack_from('<Q', data, optional_header_offset+24)[0]
else:
image_base = read_u32(data, optional_header_offset+28)
# But many disassemblers show VA as full 0x0040B330 with image base 0x400000.
# We'll compute RVA = VA - image_base
rva = VA_target - image_base
# Section headers start after optional header
section_table_off = optional_header_offset + size_optional
section_found = None
for i in range(num_sections):
off = section_table_off + i*40 # IMAGE_SECTION_HEADER size
name = data[off:off+8].rstrip(b'\x00').decode(errors='ignore')
virtual_size = read_u32(data, off+8)
virtual_address = read_u32(data, off+12)
size_of_raw = read_u32(data, off+16)
pointer_raw = read_u32(data, off+20)
if virtual_address <= rva < virtual_address + max(virtual_size, size_of_raw):
section_found = (name, virtual_address, virtual_size, pointer_raw, size_of_raw)
break
if not section_found:
raise SystemExit(f"Could not map VA 0x{VA_target:08X} (RVA 0x{rva:X}) to a section. Image base used: 0x{image_base:X}")
name, virt_addr, virt_size, ptr_raw, size_raw = section_found
file_offset = ptr_raw + (rva - virt_addr)
if file_offset + 16 > len(data):
raise SystemExit("File too small to read 16 bytes at computed file offset")
xmm = data[file_offset:file_offset+16]
print("Found section:", name)
print("Image base (from optional header): 0x%X" % image_base)
print("RVA: 0x%X -> file offset: 0x%X" % (rva, file_offset))
print("Extracted xmmword_40B330 (hex):", hexlify(xmm).decode())
# Now reuse the transformation functions to build S and invert UNK
UNK = bytes([
0x94, 0x58, 0xB2, 0x65, 0xE6, 0xF2, 0x42, 0xAF, 0x40, 0xBA,
0xE7, 0x7C, 0xA8, 0x9E, 0xA6, 0x4A, 0xA9, 0xE6, 0xB5, 0xE0,
0x77, 0x81, 0x32, 0x13, 0x0B, 0xD8, 0x57, 0x40, 0x2E, 0x7D,
0x9B, 0x33, 0xD4, 0xBB, 0x16, 0x9E, 0xD0, 0xF1, 0x43, 0x79,
0xCC, 0x7B, 0x47, 0x5D
])
def mm_cvtsi32_si128(x):
return struct.pack('<I', x) + b'\x00'*12
def mm_shuffle_epi32(vec_bytes, imm=0):
d0 = struct.unpack('<I', vec_bytes[:4])[0]
return struct.pack('<I', d0) * 4
def mm_add_epi32(a_bytes, b_bytes):
a = list(struct.unpack('<4I', a_bytes))
b = list(struct.unpack('<4I', b_bytes))
c = [ (a[i] + b[i]) & 0xFFFFFFFF for i in range(4) ]
return struct.pack('<4I', *c)
def mm_unpacklo_epi16(a_bytes, b_bytes):
a16 = list(struct.unpack('<8H', a_bytes))
b16 = list(struct.unpack('<8H', b_bytes))
out = []
for i in range(0,4):
out.append(a16[i]); out.append(b16[i])
return struct.pack('<8H', *out)
def mm_unpackhi_epi16(a_bytes, b_bytes):
a16 = list(struct.unpack('<8H', a_bytes))
b16 = list(struct.unpack('<8H', b_bytes))
out = []
for i in range(4,8):
out.append(a16[i]); out.append(b16[i])
return struct.pack('<8H', *out)
def mm_srli_epi16(a_bytes, imm):
a16 = list(struct.unpack('<8H', a_bytes))
return struct.pack('<8H', *[(x >> imm) & 0xFFFF for x in a16])
def mm_slli_epi16(a_bytes, imm):
a16 = list(struct.unpack('<8H', a_bytes))
return struct.pack('<8H', *[((x << imm) & 0xFFFF) for x in a16])
def mm_and_si128(a_bytes,b_bytes):
return bytes([a_bytes[i] & b_bytes[i] for i in range(16)])
def mm_add_epi8(a_bytes, b_bytes):
return bytes([(a_bytes[i] + b_bytes[i]) & 0xFF for i in range(16)])
def mm_sub_epi8(a_bytes, b_bytes):
return bytes([(a_bytes[i] - b_bytes[i]) & 0xFF for i in range(16)])
def mm_packus_epi16(a_bytes,b_bytes):
a16 = list(struct.unpack('<8H', a_bytes))
b16 = list(struct.unpack('<8H', b_bytes))
out = []
for x in (a16 + b16):
if x < 0: x = 0
if x > 255: x = 255
out.append(x)
return bytes(out)
def build_S(xmmword_bytes):
v48 = bytearray(256)
v7 = xmmword_bytes
v46 = mm_shuffle_epi32(mm_cvtsi32_si128(0xC), 0)
v9 = mm_srli_epi16(b'\xff'*16, 8) # mask 0x00FF per 16-bit lane
v44 = mm_shuffle_epi32(mm_cvtsi32_si128(0xF0F0F0F0), 0)
v10 = mm_shuffle_epi32(mm_cvtsi32_si128(4), 0)
v11 = mm_shuffle_epi32(mm_cvtsi32_si128(8), 0)
for i in range(16):
v12 = mm_add_epi32(v7, v10)
v13 = mm_unpackhi_epi16(v7, v12)
v14 = mm_unpacklo_epi16(v7, v12)
v15 = mm_add_epi32(v46, v7)
t1 = mm_unpacklo_epi16(v14, v13)
t2 = mm_unpackhi_epi16(v14, v13)
v16 = mm_unpacklo_epi16(t1, t2)
v17 = mm_add_epi32(v7, v11)
v18 = mm_unpacklo_epi16(v17, v15)
v19 = mm_unpackhi_epi16(v17, v15)
a = mm_and_si128(v16, v9)
t3 = mm_unpacklo_epi16(v18, v19)
t4 = mm_unpackhi_epi16(v18, v19)
b = mm_and_si128(mm_unpacklo_epi16(t3, t4), v9)
v20 = mm_packus_epi16(a, b)
v21 = mm_add_epi8(v20, v20)
v22 = mm_add_epi8(v20, mm_add_epi8(v21, v21))
const2A = mm_shuffle_epi32(mm_cvtsi32_si128(0x2A2A2A2A), 0)
temp = mm_and_si128(mm_slli_epi16(v22,4), v44)
temp2 = mm_add_epi8(v22, temp)
out = mm_sub_epi8(const2A, temp2)
v48[i*16:(i+1)*16] = out
v7 = mm_add_epi32(v7, mm_shuffle_epi32(mm_cvtsi32_si128(0x10), 0))
return bytes(v48)
def rol8(x, n):
return ((x << n) & 0xFF) | ((x >> (8-n)) & 0xFF)
def invert_transform(target_bytes, S):
invS = [0]*256
for i,v in enumerate(S):
invS[v] = i
n = len(target_bytes)
res = bytearray(n)
for i, b in enumerate(target_bytes):
t = b ^ ((i - 86) & 0xFF)
t = rol8(t, 3) # inverse of ROR3
j = invS[t] # find preimage
res[i] = j ^ 0x33
return bytes(res)
S = build_S(xmm)
unique = len(set(S))
print("Generated S unique values:", unique)
if unique != 256:
print("S is not a full permutation; aborting inversion to avoid wrong result.")
else:
flag = invert_transform(UNK, S)
print("Recovered flag bytes (hex):", hexlify(flag).decode())
try:
print("Recovered flag (utf-8):", flag.decode('utf-8'))
except:
print("Recovered flag (latin-1):", flag.decode('latin-1'))获得flag